CURVILINEAR REFORMATTED 3D INTRAOPERATIVE MR DATA USING A SIMPLE ALGORITHM TO DEMONSTRATE SUBDURAL ELECTRODE STRIP PLACEMENT
Abstract number :
1.424
Submission category :
Year :
2003
Submission ID :
581
Source :
www.aesnet.org
Presentation date :
12/6/2003 12:00:00 AM
Published date :
Dec 1, 2003, 06:00 AM
Authors :
Janaka Wansapura, Mecheri Sundaram, James Williams, Otis Williams, George Mandybur Dept pf Neurosurgery, University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, MS; Dept of Neurology, University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, MS; Dept of Radiology, Un
To interpret EEG recordings of ictal foci, the positions of the subdural electrodes relative to the cortical surface are necessary. 3D-MRI has been used to estimate the electrode position by multiplanar reformatting but is limited due to the inherent complexity of the brain[rsquo]s convolution patterns. Recently CMPR (curvilinear multiplanr reformating) using commercially available software has been introduced as a more efficient method of visualization. A simple but robust method to perform CMPR is presented.
Imaging was done on a 0.5T GE Signa SP. A fast gradient echo sequence (TR/TE = 18ms/9ms, slice thickness =1mm) was used. Imaging time was 10-12 minutes. Data were transferred to a PC workstation in DICOM format and processed using software written in MATLAB. One normal volunteer and three epilepsy patients with implanted subdural strip electrodes were studied. Processing took approximately 8 minutes to construct multiple curvilinear surfaces of the entire brain.
1: Contours of the cortical surface on a user-selected rectilinear slices were drawn. A polar coordinate system was used, where the slice axis was chosen as the Z direction.
2: Sp line fit for [italic][rho][/italic]=[italic]f([theta]) [/italic]was done for [italic][theta][/italic] ranging from [italic]0[/italic] to [italic]2[pi][/italic] at intervals of 0.01 radians for a smooth contour.
3: Taking z as the selected slice locations, fitted a surface of the form [italic][rho]=f([theta])[/italic] to the data in the non uniformly spaced vectors and linearly interpolated this surface at points specified by the desired resolution in [italic][rho],[theta][/italic],and z directions, forming a grid surface.
4: Converted the grid surface in step 3 in to Cartesian coordinates (x[apos],y[apos],z[apos]).Interpolated 3D MRI data IM=[italic] f[/italic](x,y,z) to find the pixel values of the function IM at points x[apos],y[apos],z[apos] on the curved surface.
5: To find inner layers of the cortex, changed [italic][rho] [/italic]found in step 3 by a specified length and repeated step 4.
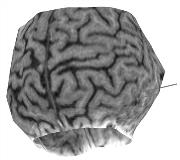
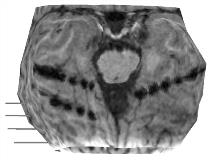
Fig.1. Lateral curvilinear reformatting shows the cortical surface and subdural strip electrodes (solid lines). Fig.2. Posterior view shows clearly the susceptibility artifacts created by three overlaying strip electrodes.
CPMR of 3D MR data is useful in visualizing the underlying cortical surface of subdural electrodes. The method described is easily implemented on a standard PC, and shown to be efficient.[figure1][figure2]